Reference Architectures
See how Moose is used in real-world analytics and data engineering scenarios.
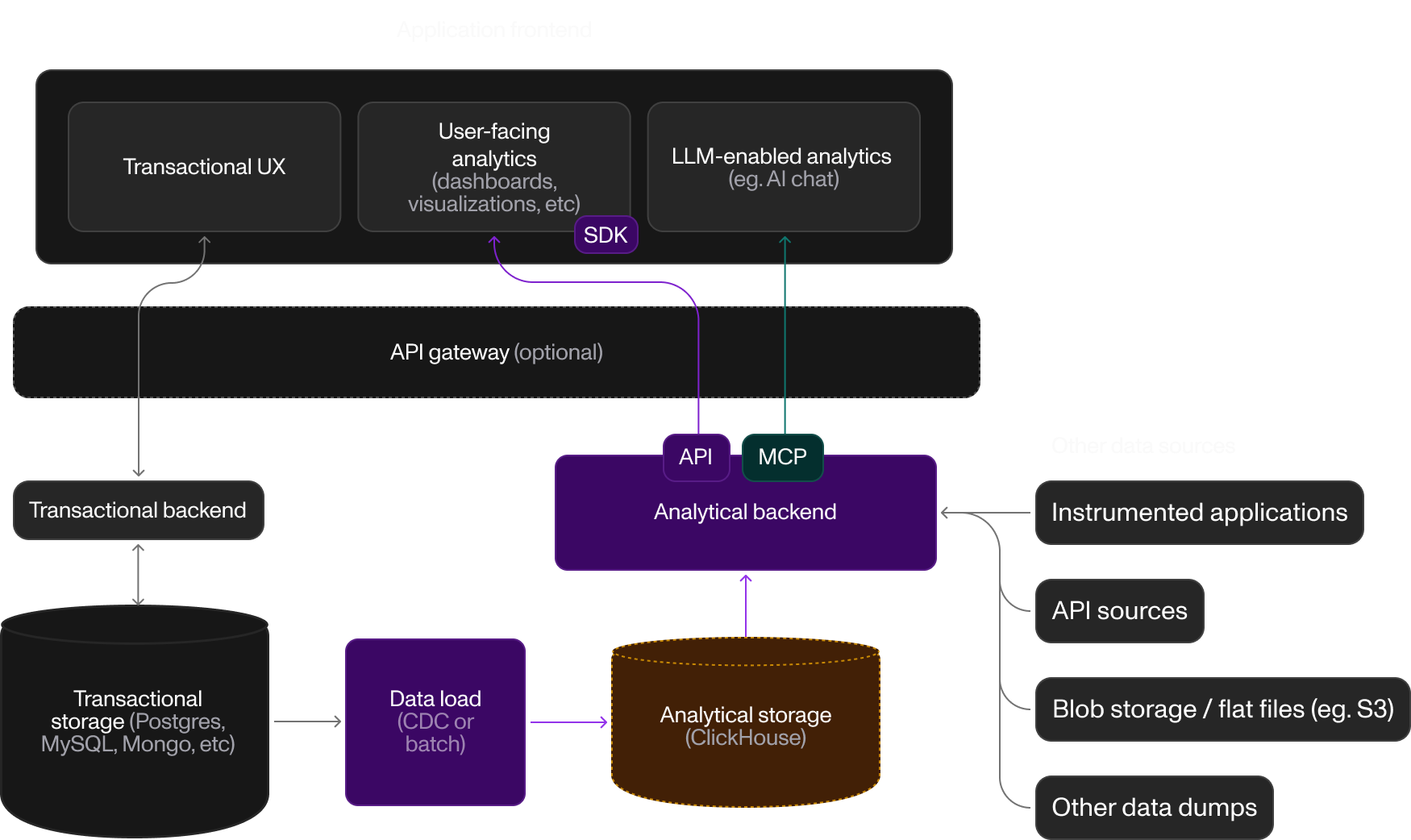
User-Facing Analytics
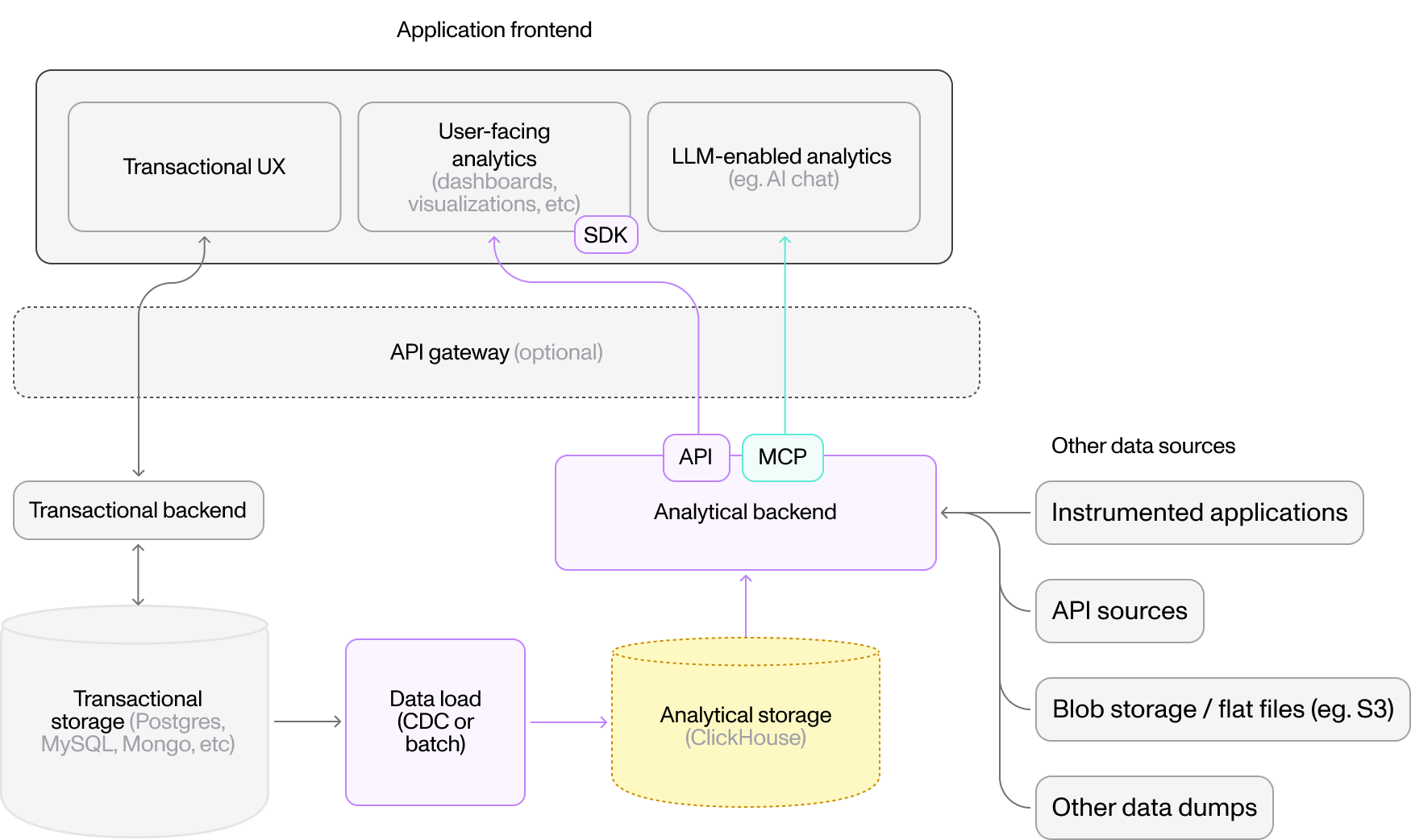
Embed real-time dashboards and metrics in your product. Moose handles event ingestion, streaming, aggregation, and exposes APIs for your frontend.
Pattern: Application → Moose → Frontend Dashboard
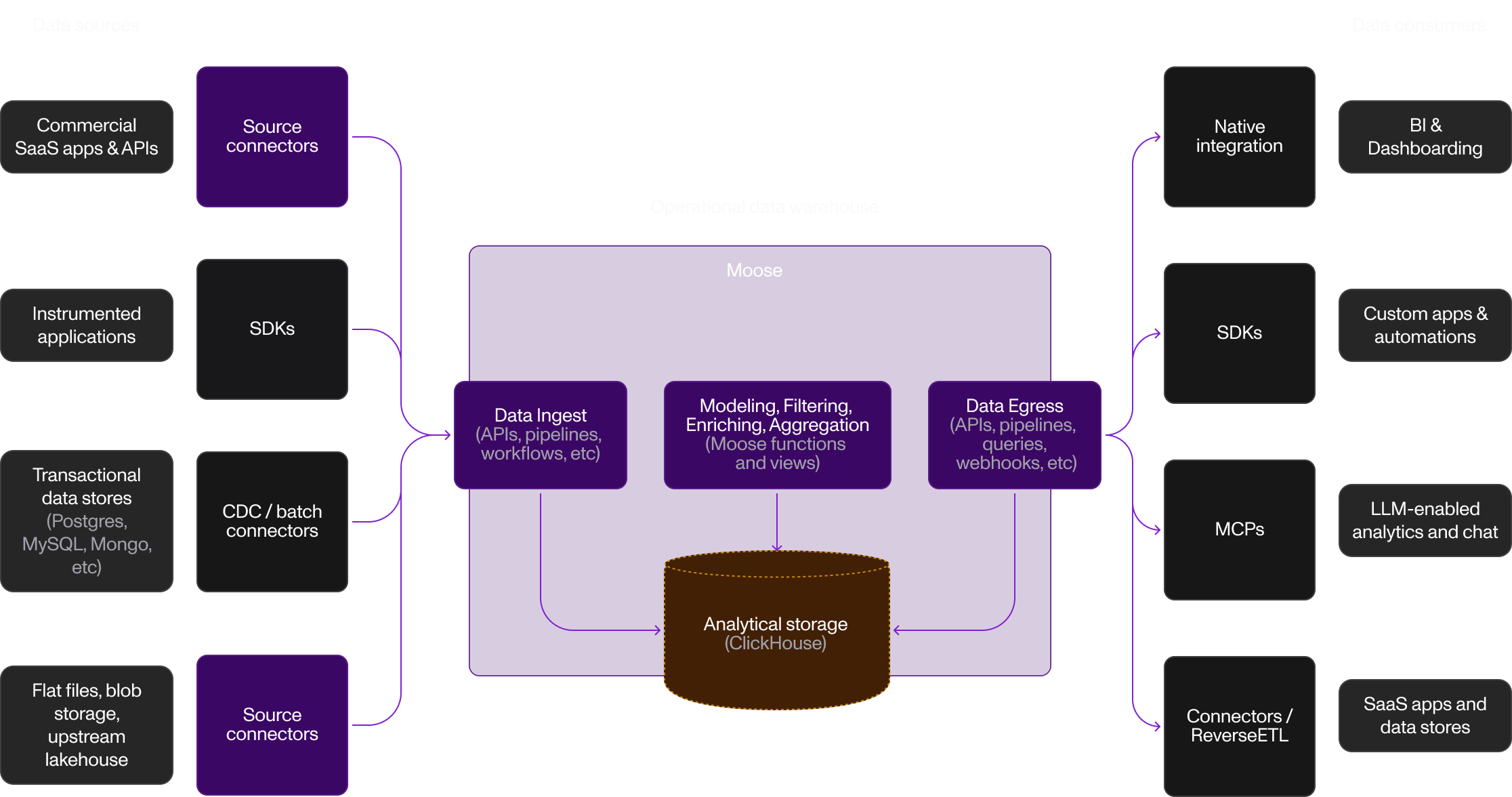
Operational Data Warehouse
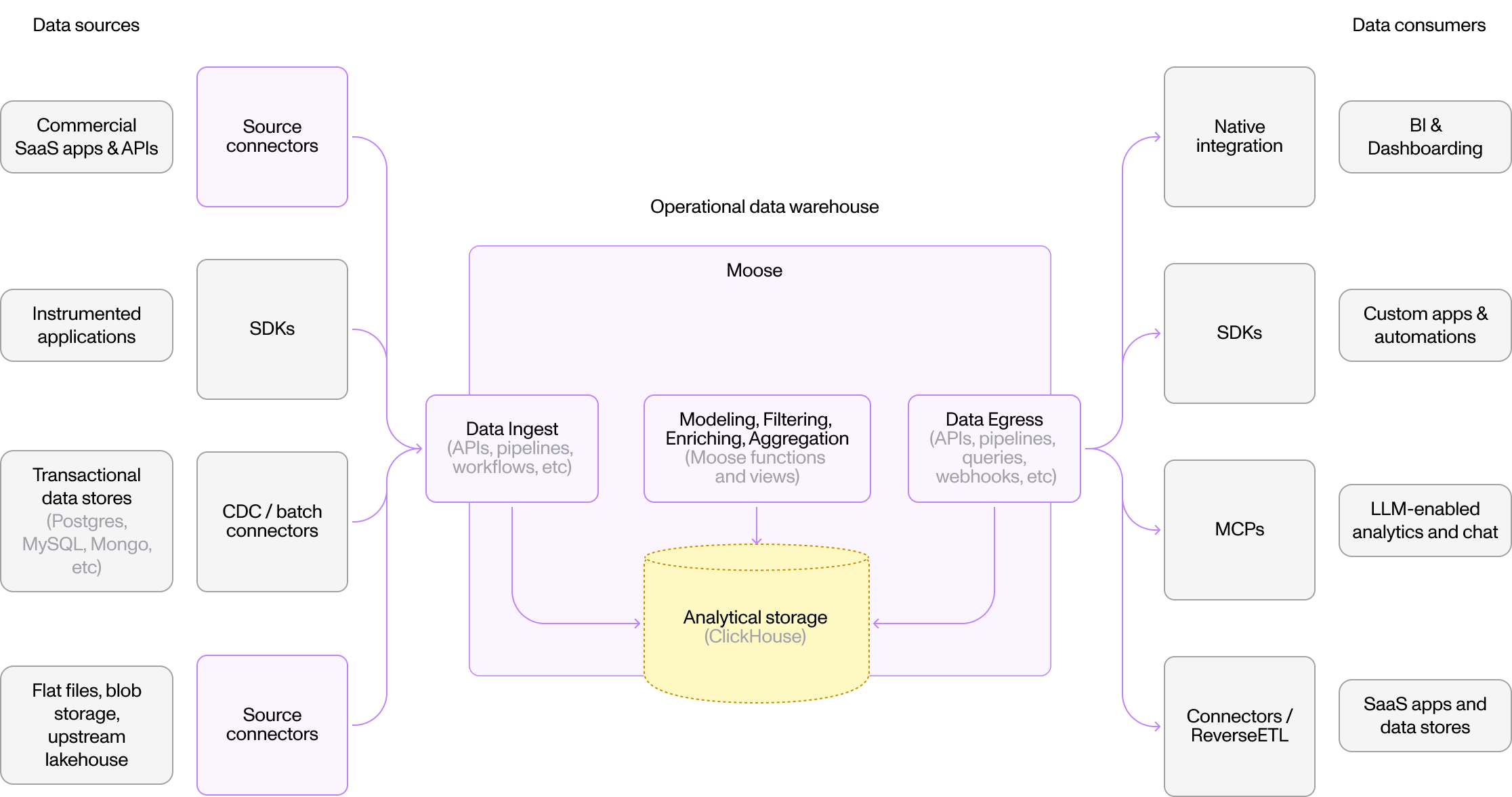
Centralize business data from SaaS, databases, and apps. Moose orchestrates ingestion, transformation, and storage in ClickHouse for BI tools.
Pattern: External APIs → Moose → BI Tools
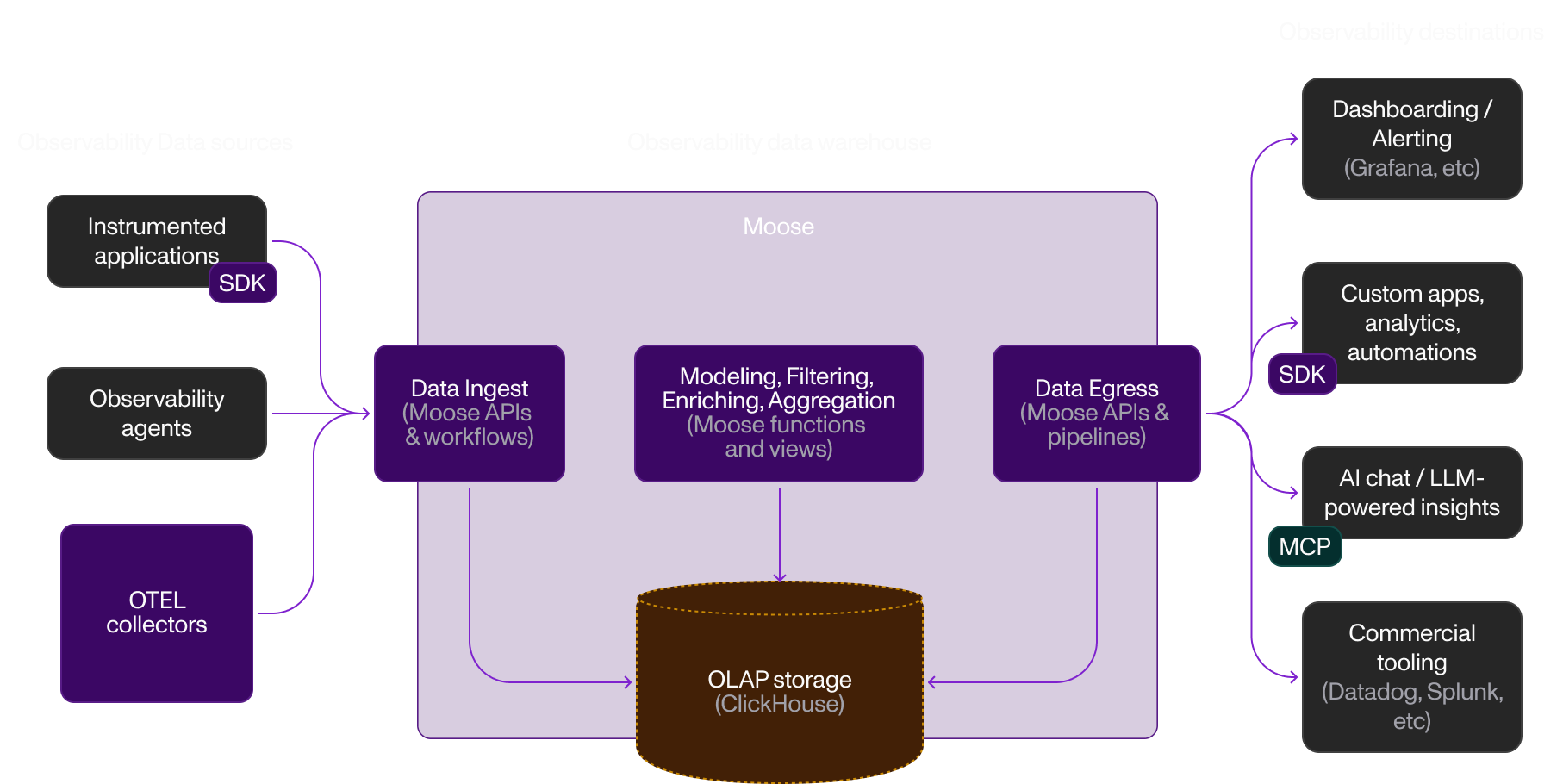
Observability
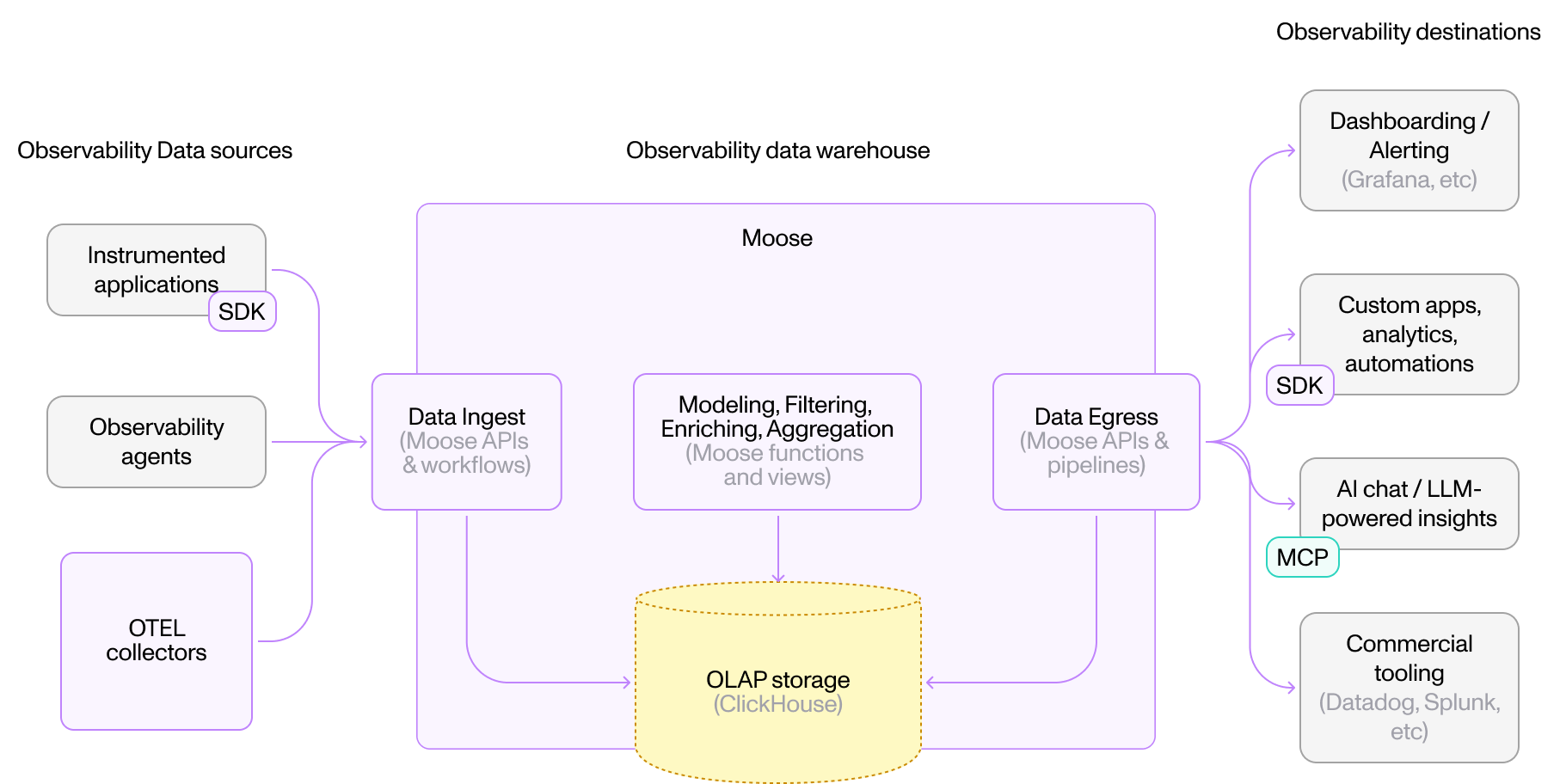
Monitor application and infrastructure metrics/logs at scale. Moose ingests telemetry, processes streams, and exposes data for monitoring platforms.
Pattern: Applications → OTEL Collector → Moose → Monitoring Tools
Configuring Infrastructure
Certain use cases may not warrant the need for all of the infrastructure that Moose provisions by default. In these cases, you can configure the infrastructure that Moose provisions by editing the moose.config.toml file:
Disabling the Streaming Engine
To disable streaming, set the streaming_engine feature flag to false in the moose.config.toml file:
[features]
streaming_engine = falseStreams won't work
Make sure you don’t have any Stream objects defined in your codebase if you disable the streaming engine.
Disabling the Temporal Workflows
To disable Temporal workflows, set the workflows feature flag to false in the moose.config.toml file:
[features]
workflows = falseWorkflows won't work
Make sure you don’t have any Workflow objects defined in your codebase if you disable the Temporal workflows.
Next Steps
- 5-Minute Quickstart — Build your first Moose pipeline
- Project Structure — Organize your Moose project for scale
Ready to build?
Head to the 5-Minute Quickstart to try Moose yourself!